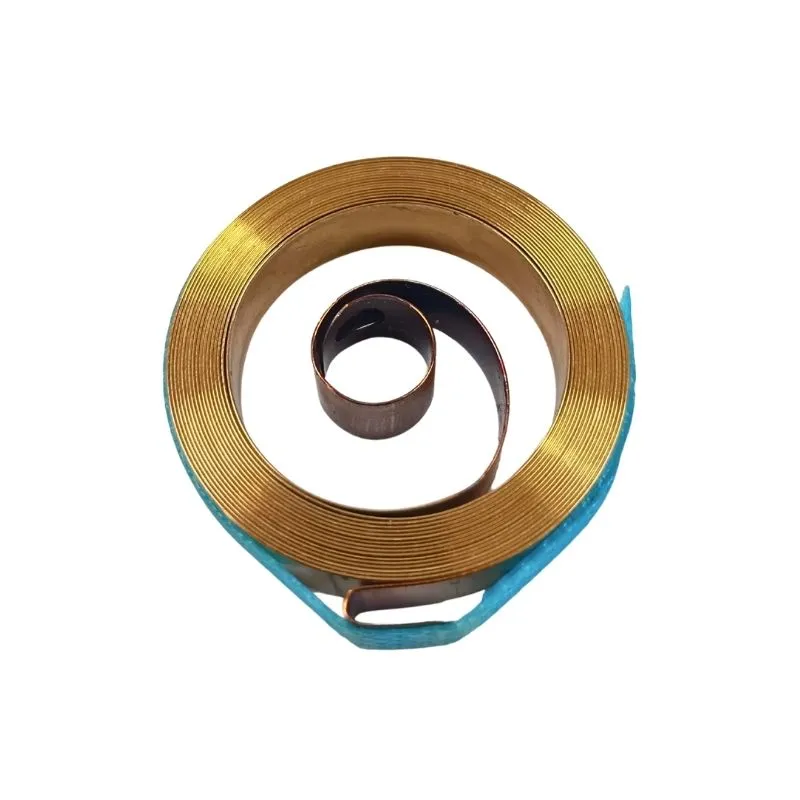
Spiral Torsion Springs
Reliable Rotational Force in a Compact Design
What Is a Spiral Torsion Spring, and How Is It Manufactured?
Spiral torsion springs are mechanical components designed to store and release energy by applying rotational force. This rotational force acts in two directions with a “return to center”. The springs deliver a linear torque per revolution. When the deflection exceeds itself, the coils begin to “close-out”, generating friction as they meet. Depending on the spring’s design, the torque will increase rapidly due to the “close-out” friction.
Spiral torsion springs are particularly effective in delivering high torque over a short rotational distance. During manufacturing, these springs are formed into a concentric spiral shape, optimizing their performance for specific applications. Using flat types of steel and their unique shape, spiral torsion springs are best suited for confined spaces.


Applications of Spiral Torsion Springs
Our constant force springs are vital components in a wide variety of industries, such as:
Medical Device

Retractable Cable for Power Banks

Windows
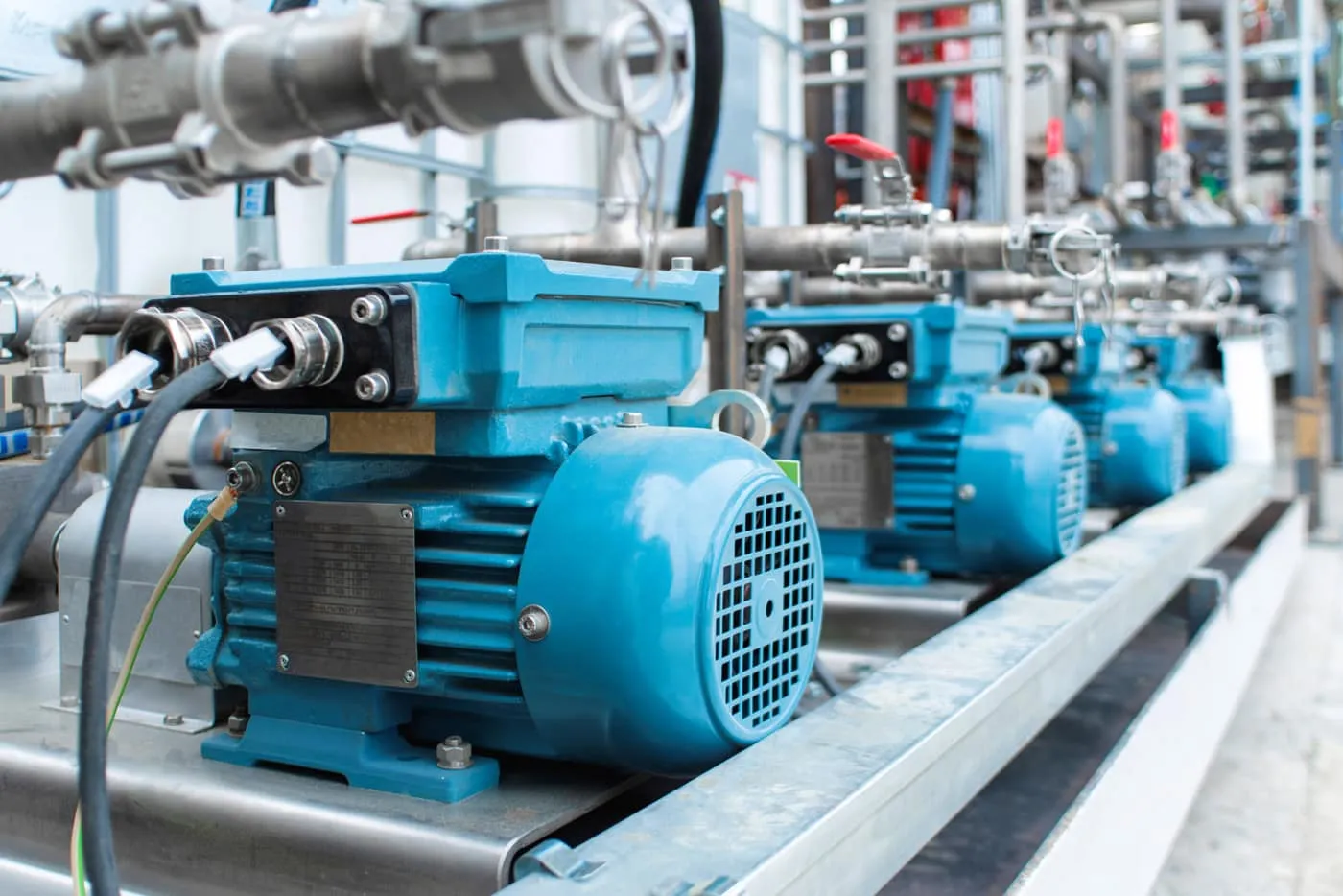
Electric Motors

Fire Dampers

Gym Equipment
Applications
In specific applications, spiral torsion springs are the ideal choice. They provide linear torque to support lift, rotational movement, and closing or opening force for various industries.
Motor Brush Assemblies
The spiral torsion spring plays a crucial part in the longevity and efficiency of electric motors by:
Maintaining consistent pressure on carbon brushes responsible for conducting electrical current between the stationary and rotating parts.
Ensuring carbon brushes remain in optimal contact with the commutator.
Industrial
Due to their store and release of rotational energy, spiral torsion springs are found in:
Clutches and brakes
Retractable mechanisms
Valves and actuators
Counterbalance systems
Conveyor systems
Recoil mechanisms
Rotary dampers
Winding and rewinding devices
They maintain consistent torques and tension in compact spaces, generate a rotational force and perform consistently under heavy loads.
Dental X-ray Head Unit
By counterbalancing the weight of the X-ray head and enabling smooth, stable positioning, spiral torsion springs improve both the functionality and ergonomics of dental X-ray head units. They provide controlled movement and positioning of the X-ray head.
Jet Stairs or Main Door
Work as counterbalances for smooth deployment of stairs, reducing operator effort, stability and control. For main aircraft doors, spiral torsion springs assist in opening and closing, maintaining door position and emergency door operation. They reduce the wear and tear on components, ensuring smooth operation, reduced force requirement, increased safety, and enhanced durability.
Armored Hatch Covers
Commonly used in military vehicles, tanks, and other armored equipment. Spiral torsion springs enhance the functionality, safety, and usability of the heavy protective covers. They are integrated into the hinge mechanism of armored hatch covers that assist in the opening and closing process. Counterbalancing the weight of the hatch, they maintain stability and position, support emergency operation, reduce wear and tear on the hinge mechanism, noise reduction (opening and closing hatch), and support motorized or hydraulic systems.
Cargo Doors
Used in various industries, including aviation, automotive, and shipping, to facilitate smooth and controlled opening and closing. Crucial to managing the heavy weight of cargo doors while ensuring safety and ease of operation.
Motor Assist for Robotic Joints
Enhances the functionality, efficiency, and precision of robotic movements. Spiral torsion springs play a crucial role in balancing forces, reducing motor workload, and improving energy efficiency. Precision and control, especially in complex or multi-axis joints. Reduced motor size, weight of device, and power requirements. Soft robotics and adaptive motion, energy efficiency and conservation, safety and impact absorption, and increased durability and reduced maintenance.
Trailer Tarp Systems
Assist in the deployment and retraction of the tarp while counterbalancing the weight with controlled movement.
Benefits of Spiral Torsion Springs
Where Great Work Meets Great Rewards
Compact and efficient energy storage
High torque with minimal rotation
Versatility and customizability
Versatility and customizability
Versatility and customizability
Durability and longevity
Protection and resilience
Spiral Torsion Springs
Spiral torsion springs, also known as clock springs or hair springs, are mechanical devices that twist along their axis. These springs are tightly wound and can generate high torque or rotational force, making them ideal for applications where space is limited and precise mechanical performance is essential.
Click to expand the graphic and see how the spring can interact with your products.
Spiral Torsion Spring Life & Performance Considerations
The life of a spiral torsion spring is rated by the number of cycles it can perform before signs of fatigue, deformation, or loss of torque begin to appear. Depending on material, design, and operating conditions, these springs can achieve a life cycle range from several thousand to well over a million cycles.
Spring life varies and is dependent on the specific application, as well as the following performance considerations:
Stainless steel, high-carbon steel, or specialty alloys provide different fatigue resistance and environmental durability.
Proper lubrication reduces internal friction and wear.
Certain chemicals can corrode or weaken spring materials if not properly matched to the environment.
High or low temperatures can impact material elasticity, torque output, and fatigue life.
Rapid changes in motion place additional dynamic stress on the spring, potentially reducing its cycle life.
Materials
Various materials for projects or prototypes with distinct advantages:
◉ Carbon Steel – may require pre-galvanized coatings or additional corrosion protection.
◉ Stainless Steel – excellent heat and corrosion resistance properties.
◉ Specialty Alloys – metals such as chromium alloys and cold-drawn nickel are best for applications requiring high corrosion resistance when exposed to extreme temperatures.
301 Stainless Steel
An austenitic chromium-nickel type of stainless steel that can be cold-worked to achieve high ductility and tensile strength. It does not harden by heat treatment, and although it is not magnetic in the annealed state, it does become magnetic with cold deformation.
Inconel
Inconel springs are ideal for use in corrosive environments exposed to salt water, aggressive air, or aggressive water conditions.
High Carbon Steel
Features significant hardness, due to more than 0.3% carbon content.
Mounting Methods
Hubs or collets, tabs and keyways, hooks and pin, hook and slot mounted on.
Clamped- not free to move or hinged- free to move.